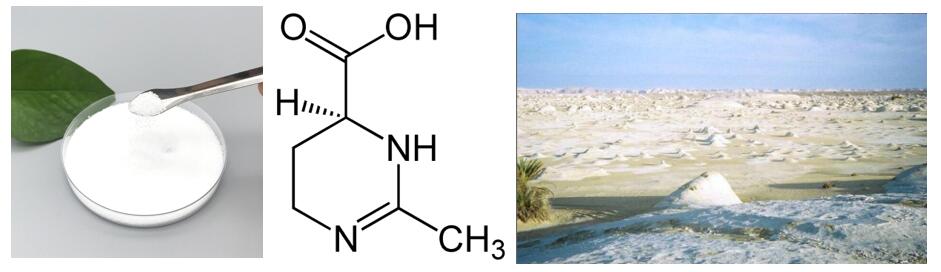
New Internet Celebrity Cosmetic Active Ingredient – Ectoine
Ectoine, whose chemical name is tetrahydromethylpyrimidine carboxylic acid/tetrahydropyrimidine, is an amino acid derivative. The original source is a salt lake in the Egyptian desert that in extreme conditions (high temperatures, drought, strong UV radiation, high salinity, osmotic stress) desert halophilic bacteria produce a natural protective component in the outer layer of the cell. Ectoine can be found in nature in a large number of different bacteria, which produce it precisely for the reasons mentioned earlier. Of course, such an exceptional protective effect on the species that produce it has prompted numerous studies on the potential use of ectoine in humans.
Ectoine benefits for skin care:
1.Moisturizing
One of the reasons why Ectoine can allow halophilic bacteria to survive in extreme environments is that it can regulate osmotic pressure.It is a very strong hydrophilic substance. Although the molecular weight is small, it can form a “hydration shell” around cells and proteins by combining with water molecules in the surrounding environment, similar to a stable protective film. To reduce the loss of skin moisture.
2.Improve skin’s protective ability
It is precisely because Ectoine can combine with water molecules to form a protective shell, so in addition to preventing the loss of skin moisture, it can also be used as a “city wall” to protect the skin from external stimulation and damage, nourish and stabilize the skin, and strengthen the skin The ability to resist ultraviolet rays and pollution.
3.Repair and soothing
Ectoine is also a very useful repairing ingredient, especially when you experience skin sensitivity, barrier damage, acne breakage, and redness after sunburn. Choosing this ingredient can have a certain soothing effect. The fragility and discomfort of the skin will be gradually improved.